About AD
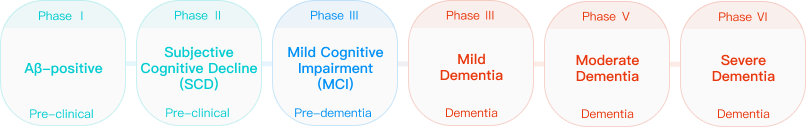
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), an insidious neurodegenerative ailment, unfolds with a clandestine onset and progressive deterioration, comprising preclinical, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and dementia stages. During the preclinical phase, patients typically manifest no overt cognitive decline or merely exhibit subjective cognitive descent. In the MCI stage, patients begin to experience cognitive impairments, particularly in memory. In the dementia stage, individuals gradually forfeit fundamental life capabilities, profoundly impacting the mental and physical well-being of the middle-aged and elderly, imposing a substantial burden on families and society.
With the ongoing escalation of population aging in China, the populace of AD patients is rapidly proliferating. A 2022 report from the international medical journal “The Lancet Public Health” reveals that there are presently approximately 10 million AD patients in China, with an anticipated surge to 30 million by 2030. Due to the limited awareness of the disease among patients and their families, coupled with the constrained diagnostic methods offered by hospitals, numerous patients are unable to receive timely diagnosis and treatment.
Urgent measures are to needed enhance the diagnosis and treatment of AD in response to the escalating burden of the disease in China, compounded by low rates of diagnosis and treatment.